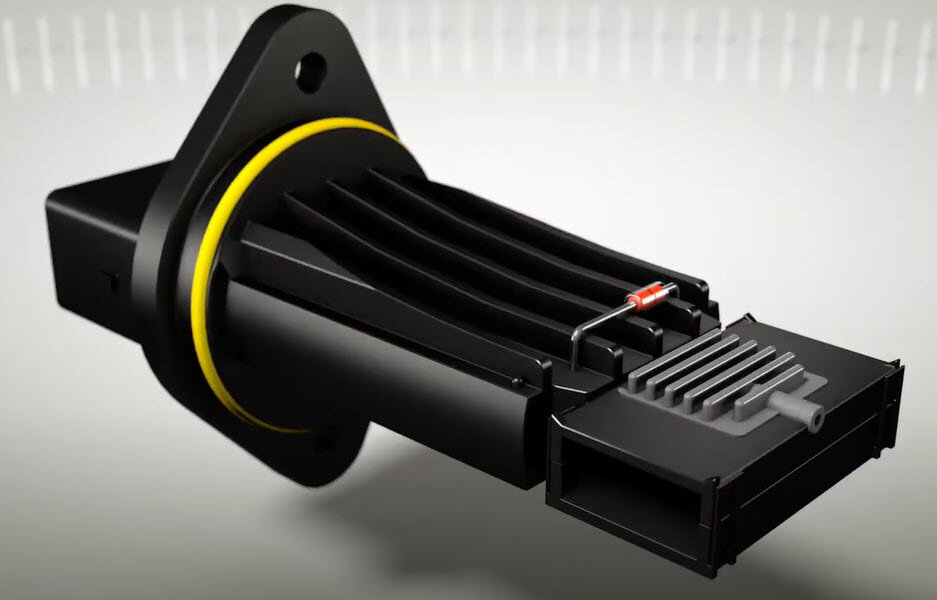
The air mass sensor , also known as the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor , is a crucial component in your vehicle’s engine management system. It measures the amount of air entering the engine and sends this data to the Engine Control Unit (ECU). The ECU then adjusts the air-fuel mixture to ensure optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control.
However, like any other part, the air mass sensor can fail over time. When it does, it can lead to a host of problems that affect your vehicle’s drivability and overall performance. In this guide, we’ll explore the common reasons why an air mass sensor fails, the symptoms to watch for, and how to address the issue.
What Is an Air Mass Sensor?
Before diving into why the air mass sensor fails, let’s briefly review its role. The air mass sensor is typically located between the air filter and the intake manifold. It measures the volume and density of air entering the engine and converts this information into an electrical signal sent to the ECU. This data is essential for calculating the correct amount of fuel needed for combustion.
Without accurate readings from the air mass sensor, the ECU cannot maintain the ideal air-fuel ratio, leading to poor engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and higher emissions.
Common Causes of Air Mass Sensor Failure
Several factors can contribute to the failure of an air mass sensor. Understanding these causes can help you prevent issues and extend the life of the sensor.
1. Contamination
One of the most common reasons for air mass sensor failure is contamination. Over time, dirt, oil, and debris from the air intake system can accumulate on the sensor’s delicate wires or film. This buildup interferes with its ability to measure airflow accurately.
- How It Happens: Poor-quality air filters, improper installation of aftermarket parts, or neglecting to replace the air filter regularly can allow contaminants to reach the sensor.
2. Electrical Issues
The air mass sensor relies on electrical connections to communicate with the ECU. Corroded, loose, or damaged wiring can disrupt this communication, causing the sensor to malfunction.
- Signs of Electrical Problems: Frayed wires, corroded terminals, or intermittent connectivity issues are often the culprits.
3. Excessive Heat
The air mass sensor operates in a high-temperature environment near the engine. Prolonged exposure to excessive heat can damage its internal components, reducing its accuracy or causing complete failure.
- Risk Factors: A faulty cooling system or driving in extreme conditions can exacerbate heat-related issues.
4. Age and Wear
Like all mechanical and electronic components, the air mass sensor has a limited lifespan. Over time, its sensitive elements can degrade due to normal wear and tear, especially in vehicles with high mileage.
5. Incorrect Cleaning
Attempting to clean the air mass sensor with improper tools or chemicals can cause irreversible damage. For example, using harsh cleaners or compressed air can destroy the delicate wires or film inside the sensor.
6. Backfires in the Intake System
A backfire occurs when unburned fuel ignites in the intake manifold. This sudden explosion can send a shockwave through the intake system, damaging the air mass sensor.
- Causes of Backfires: Lean air-fuel mixtures, faulty ignition systems, or timing issues are common triggers.
Symptoms of a Failing Air Mass Sensor
When the air mass sensor begins to fail, it can cause a variety of noticeable symptoms. Here are some of the most common signs:
1. Check Engine Light Illuminated
A malfunctioning air mass sensor often triggers the Check Engine Light. The ECU detects irregularities in the airflow readings and stores a diagnostic trouble code (DTC), such as P0101, P0102, or P0103.
2. Reduced Fuel Efficiency
If the sensor provides inaccurate data, the ECU may deliver too much or too little fuel, leading to poor mileage. You may notice that you’re filling up the tank more frequently than usual.
3. Rough Idling or Stalling
A failing air mass sensor can cause the engine to idle roughly or stall unexpectedly. This happens because the ECU cannot maintain the correct air-fuel mixture at low speeds.
4. Loss of Power and Acceleration
You may experience sluggish acceleration or a noticeable drop in engine power, especially during heavy loads or uphill driving. This is often due to incorrect fuel delivery.
5. Black Smoke from Exhaust
In severe cases, a faulty air mass sensor can cause excessive fuel to enter the combustion chamber, resulting in black smoke from the exhaust. This is a sign of incomplete combustion.
6. Hard Starting
If the sensor fails completely, the engine may struggle to start or require multiple attempts to ignite. This is because the ECU cannot determine the correct amount of air entering the engine.
How to Diagnose a Faulty Air Mass Sensor
If you suspect your air mass sensor is failing, here are some steps to diagnose the issue:
- Scan for Error Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve trouble codes related to the air mass sensor.
- Inspect the Sensor: Remove the sensor and visually check for dirt, oil, or damage. Look for signs of contamination or physical wear.
- Test the Sensor: Use a multimeter to measure the sensor’s voltage and resistance. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Check Wiring and Connections: Inspect the wiring harness and connectors for corrosion, looseness, or damage.
Solutions for a Faulty Air Mass Sensor
Once you’ve confirmed that the air mass sensor is faulty, here are some steps you can take to resolve the issue:
1. Clean the Sensor
If contamination is the problem, cleaning the sensor may restore its functionality. Use a specialized MAF sensor cleaner to remove dirt and oil without causing damage.
2. Replace the Sensor
If cleaning doesn’t solve the issue, replacing the sensor is often the best solution. Look for a high-quality replacement to ensure reliable performance.
3. Address Underlying Issues
Before installing a new sensor, inspect the air intake system for other problems, such as clogged air filters or vacuum leaks. Fixing these issues can prevent premature failure of the new sensor.
4. Perform Regular Maintenance
Regularly replace air filters, use high-quality fuel, and keep the engine bay clean to reduce the risk of sensor failure.
Preventing Air Mass Sensor Problems
Prevention is key to avoiding costly repairs. Here are some tips to extend the life of your air mass sensor:
- Use High-Quality Air Filters: Clean air filters prevent contaminants from reaching the sensor (Source: Automotive Service Association).
- Avoid Improper Cleaning: Never use compressed air or harsh chemicals to clean the sensor.
- Keep Electrical Connections Secure: Regularly inspect and clean wiring and connectors to prevent corrosion.
- Follow Maintenance Schedules: Stick to your vehicle’s recommended maintenance schedule to catch potential issues early.
Conclusion
The air mass sensor plays a vital role in ensuring your engine runs smoothly and efficiently. By understanding the common causes of failure, recognizing the symptoms, and taking preventive measures, you can avoid costly repairs and keep your vehicle performing at its best. Whether you’re diagnosing an issue or simply performing routine maintenance, paying attention to this critical component can save you time and money in the long run.
Have questions about your air mass sensor or need advice on replacements? Leave a comment below—we’re here to help!
Disclaimer: Always consult a professional mechanic if you’re unsure about diagnosing or repairing complex components like the air mass sensor.
Sources
- Automotive Service Association. (n.d.). Importance of Air Filtration in Vehicle Maintenance . Retrieved from https://www.asashop.org/