The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve is a critical component in modern diesel and gasoline engines. Its primary function is to reduce harmful emissions by recirculating a portion of the engine’s exhaust gases back into the intake manifold. This process lowers combustion temperatures, which helps minimize the production of nitrogen oxides (NOx), a major contributor to air pollution.
However, like any mechanical part, the EGR valve can fail over time. When it does, it can lead to reduced engine performance, increased emissions, and even costly repairs if left unchecked. So, what causes an EGR valve to fail? Let’s break it down.
1. Carbon Build-Up
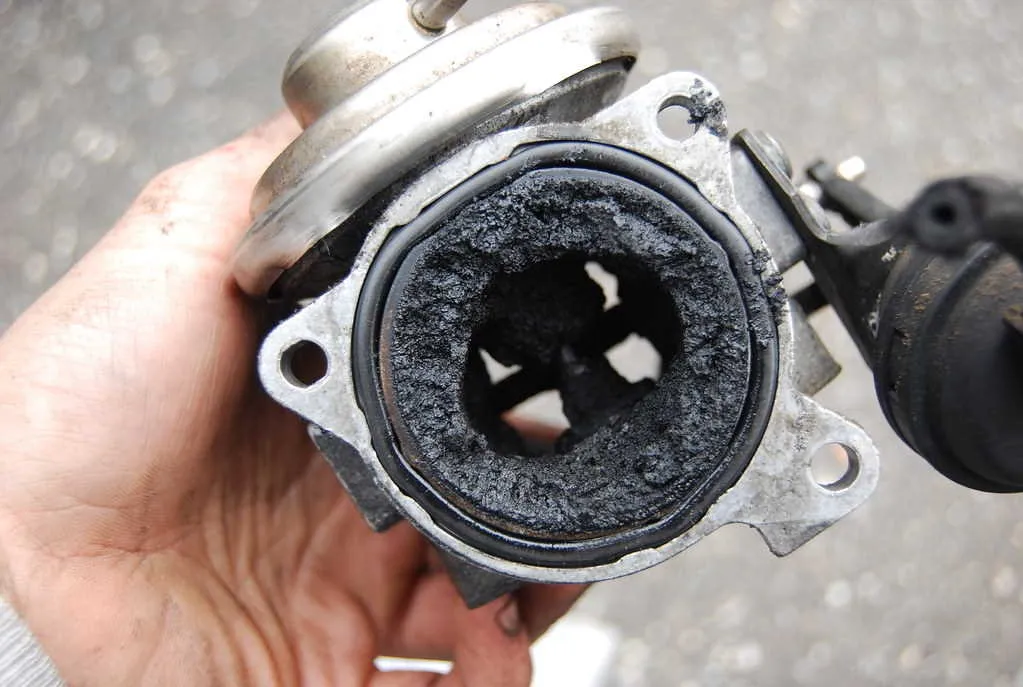
One of the most common reasons for EGR valve failure is carbon build-up . Over time, the exhaust gases that pass through the valve contain small amounts of carbon particles, oil residues, and soot. These deposits can accumulate on the valve and its passages, causing it to stick open, close improperly, or become completely blocked.
- Symptoms of Carbon Build-Up:
- Rough idling or stalling.
- Reduced engine power.
- Check Engine Light (CEL) illuminated.
- Increased fuel consumption.
To prevent this issue, regular cleaning of the EGR valve is recommended, especially in vehicles with high mileage or those frequently driven in stop-and-go traffic. You can find effective EGR cleaning kits here to help maintain your valve and keep it functioning properly.
2. Poor Quality Fuel
Using low-quality or contaminated fuel can accelerate wear and tear on the EGR valve. Inferior fuels often contain higher levels of impurities, such as sulfur and other contaminants, which contribute to carbon deposits and corrosion within the valve and its components.
- Solution: Always opt for high-quality, clean diesel or gasoline, and consider using fuel additives designed to clean the fuel system and reduce carbon build-up. A popular choice among vehicle owners is this fuel system cleaner, which can help prolong the life of your EGR valve and other engine components.
3. Oil Contamination
In some engines, excessive oil entering the intake system, often due to worn piston rings, valve seals, or turbocharger issues, can lead to oil contamination in the EGR system. This oil mixes with exhaust gases and creates a sticky residue that clogs the valve and restricts its movement.
- Symptoms of Oil Contamination:
- Thick, sludgy deposits inside the EGR valve.
- Engine misfires or hesitation.
- Smoke from the exhaust.
If you notice these symptoms, it’s worth investigating the root cause of the oil contamination to prevent further damage. For example, replacing worn gaskets or seals with high-quality replacements like these premium gasket kits can help address underlying issues.
4. Electrical or Vacuum Issues
Many modern EGR valves are electronically controlled, relying on sensors and actuators to regulate the flow of exhaust gases. If there’s a problem with the electrical connections, wiring, or vacuum lines, the valve may not function properly.
- Common Electrical/Vacuum Problems:
- Faulty sensors sending incorrect signals to the EGR valve.
- Damaged wiring or corroded connectors.
- Leaking or disconnected vacuum hoses.
These issues can cause the EGR valve to remain stuck in one position, leading to poor engine performance or triggering fault codes. Replacing damaged sensors or vacuum lines with reliable parts, such as this vacuum hose kit , can help restore proper functionality.
5. Overheating
Excessive heat can also cause an EGR valve to fail. The valve operates in a high-temperature environment, and prolonged exposure to extreme heat can warp its components or degrade the internal seals. This is especially common in engines that run hot due to cooling system problems or heavy loads.
- Signs of Overheating:
- Warped or cracked valve housing.
- Seals that no longer seal properly.
- Persistent overheating warnings on the dashboard.
Regular maintenance of your vehicle’s cooling system can help mitigate this risk. Consider upgrading to a high-performance radiator or coolant, such as this advanced coolant solution , to keep your engine running cooler and protect sensitive components like the EGR valve.
6. Age and Wear
Like all mechanical parts, EGR valves have a limited lifespan. Over time, the constant opening and closing of the valve can cause wear on its moving parts, while exposure to heat and exhaust gases can degrade its materials. Eventually, the valve may fail due to simple old age.
- How Long Does an EGR Valve Last?
- Typically, an EGR valve can last between 50,000 to 100,000 miles, but this varies depending on driving conditions, maintenance habits, and the quality of the valve itself.
When it’s time to replace your EGR valve, opting for a durable replacement like this highly-rated EGR valve can ensure long-lasting performance and reliability.
7. Incorrect Installation or Repairs
If the EGR valve has been replaced or repaired incorrectly, it may not function as intended. For example, failing to clean the intake manifold during a replacement can allow existing carbon deposits to re-enter the new valve, causing premature failure.
- Tips for Proper Installation:
- Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.
- Clean the surrounding components thoroughly before reinstalling the valve.
- Use genuine or high-quality aftermarket parts.
How to Diagnose a Failing EGR Valve
If you suspect your EGR valve is failing, here are some steps to diagnose the issue:
- Check for Warning Lights: A malfunctioning EGR valve often triggers the Check Engine Light (CEL).
- Scan for Error Codes: Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the EGR system. A reliable option is this compact OBD-II scanner , which makes diagnosing issues quick and easy.
- Inspect the Valve: Remove the EGR valve and visually inspect it for carbon build-up, cracks, or damage.
- Test Functionality: Manually test the valve’s operation (if possible) or use diagnostic tools to check its response to commands from the engine control unit (ECU).
Preventing EGR Valve Failure
While some degree of wear is inevitable, you can take steps to extend the life of your EGR valve:
- Use High-Quality Fuel: Cleaner fuel reduces carbon deposits and minimizes wear.
- Perform Regular Maintenance: Clean the EGR valve periodically, especially in older vehicles or those used for heavy-duty tasks.
- Address Underlying Issues: Fix problems like oil leaks, cooling system failures, or sensor malfunctions promptly to avoid secondary damage to the EGR valve.
- Drive Smart: Avoid short trips and frequent idling, as these conditions promote carbon build-up.
Conclusion
Understanding what causes an EGR valve to fail can save you time, money, and frustration in the long run. By addressing common culprits like carbon build-up, poor-quality fuel, and overheating, you can keep your engine running smoothly and reduce the likelihood of expensive repairs. Whether you’re looking to clean, repair, or replace your EGR valve, there are plenty of solutions available to help you get the job done right.
Have questions about your EGR valve or need advice on replacements? Leave a comment below—we’re here to help!
Disclaimer: Always consult a professional mechanic if you’re unsure about diagnosing or repairing complex components like the EGR valve.