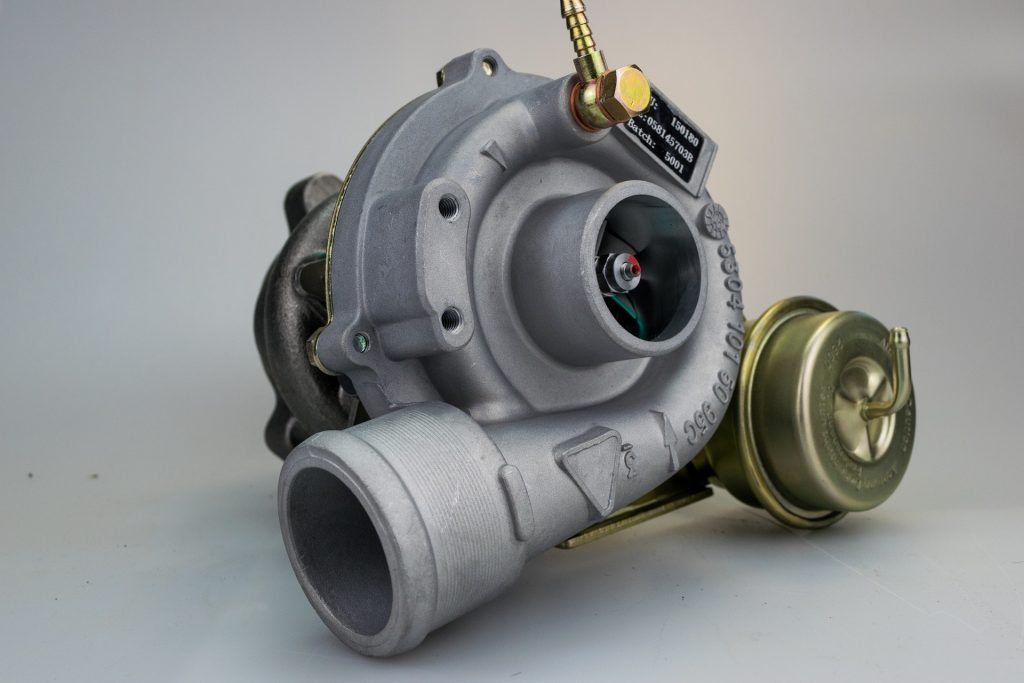
The turbocharger is a vital component in modern diesel and gasoline engines, designed to boost performance, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce emissions. However, like any mechanical part, it can develop issues over time. Identifying turbocharger problems early can save you from costly repairs and ensure your vehicle continues to perform at its best. In this guide, we’ll explore the common symptoms of turbocharger failure, their underlying causes, and how to address them effectively.
Why Turbocharger Problems Occur
Before diving into the symptoms, it’s important to understand why turbochargers fail. Here are some of the most common causes:
1. Oil Starvation
Turbochargers rely on a steady supply of clean oil to lubricate their bearings and cool the turbine. If the oil supply is restricted due to clogged lines, low oil levels, or poor-quality oil, the turbocharger can overheat and seize.
2. Contaminated Oil
Dirty or degraded oil can introduce abrasive particles into the turbocharger’s delicate components, leading to premature wear and damage.
3. Overheating
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause the turbocharger’s internal components to warp or degrade, especially if the cooling system is not functioning properly.
4. Wear and Tear
Like all mechanical parts, turbochargers have a limited lifespan. Over time, components such as seals, gaskets, and bearings can wear out, leading to leaks or reduced performance.
5. Improper Installation
Incorrect fitting during a turbocharger replacement—such as failing to replace gaskets or flush the oil system—can lead to leaks, oil starvation, or other issues.
Common Symptoms of Turbocharger Problems
Recognizing the signs of turbocharger failure is the first step toward addressing the issue. Here are the most common symptoms to watch for:
1. Loss of Power
One of the most noticeable signs of turbocharger failure is a significant drop in engine power. You may experience sluggish acceleration, difficulty maintaining speed, or reduced towing capacity.
2. Excessive Exhaust Smoke
Changes in exhaust smoke color or density can indicate turbocharger issues:
- Blue Smoke: Suggests oil leaking into the combustion chamber, often caused by worn seals or gaskets.
- Black Smoke: Indicates unburned fuel due to improper air-fuel mixing, which can result from a malfunctioning turbocharger.
- White Smoke: May point to coolant entering the combustion chamber, though this is less common with turbocharger problems.
3. Whistling or Squealing Noises
A high-pitched whistling or squealing noise under acceleration often points to a damaged turbocharger impeller or a leak in the intake or exhaust system.
4. Check Engine Light Illuminated
Modern vehicles are equipped with sensors that monitor turbocharger performance. If the ECU detects irregularities, it will trigger the Check Engine Light and store diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) such as P0299 (underboost) or P0234 (overboost).
5. Oil Leaks
Oil leaks around the turbocharger housing or connections are another common symptom. These leaks can occur due to worn seals or gaskets and should be addressed immediately to prevent further damage.
6. Delayed Throttle Response
Turbo lag—the delay between pressing the accelerator and feeling the turbocharger kick in—is normal to some extent. However, excessive lag or hesitation may indicate a problem with the turbocharger or its associated components.
How to Diagnose Turbocharger Problems
If you suspect your turbocharger is failing, here are some steps to diagnose the issue:
1. Scan for Error Codes
Use an OBD-II scanner to retrieve diagnostic trouble codes related to turbocharger performance. Common codes include:
- P0299: Turbocharger underboost condition
- P0234: Turbocharger overboost condition
- P0243: Turbocharger wastegate solenoid malfunction
2. Inspect for Physical Damage
Check the turbocharger housing, hoses, and connections for signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Pay special attention to the oil feed and drain lines, as blockages here can starve the turbocharger of oil.
3. Test Boost Pressure
Use a boost pressure gauge to measure the turbocharger’s output. Compare the readings to your vehicle’s specifications. Low boost pressure may indicate a failing turbocharger, while excessive boost could point to overboost conditions.
4. Listen for Unusual Noises
Pay attention to any whistling, squealing, or grinding sounds during operation. These noises often indicate problems such as a damaged impeller, leaks in the intake or exhaust system, or bearing failure.
5. Check Oil Levels and Quality
Ensure the engine has adequate oil and that the oil is clean and free of contaminants. Dirty or degraded oil can accelerate turbocharger wear and lead to failure.
Solutions for Turbocharger Problems
Once you’ve identified the issue, here are some steps you can take to resolve it:
1. Clean or Replace the Turbocharger
If contamination is the problem, cleaning the turbocharger may restore its functionality. For more severe issues, replacing the turbocharger with a high-quality replacement unit is often the best solution.
2. Replace Worn Components
Inspect and replace worn components such as gaskets, seals, and oil lines to prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance.
3. Flush the Oil System
Before installing a new turbocharger, flush the engine’s oil system to remove any debris or contaminants. Consider using a high-quality engine flush solution to ensure the system is clean.
4. Address Underlying Issues
If the turbocharger failed due to overheating or oil starvation, address the root cause of the problem. For example, repair the cooling system or fix oil feed line blockages to prevent future failures.
Preventing Turbocharger Problems
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some tips to extend the life of your turbocharger:
- Use High-Quality Oil: Clean, high-quality oil reduces the risk of contamination and ensures proper lubrication.
- Perform Regular Maintenance: Stick to your vehicle’s recommended service schedule, including oil changes and filter replacements.
- Allow Proper Cool-Down Time: After driving, let the engine idle for a minute or two before turning it off. This allows the turbocharger to cool down and prevents oil coking.
- Inspect Regularly: Check the turbocharger and its components during routine maintenance to catch potential issues early.
Conclusion
Identifying turbocharger problems early can save you from costly repairs and ensure your vehicle continues to perform at its best. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and taking preventive measures, you can keep your turbocharger in top condition. Whether you’re diagnosing an issue or performing routine maintenance, paying attention to your turbocharger can save you time and money in the long run.
Have questions about turbocharger problems or need advice on replacements? Leave a comment below—we’re here to help!
Disclaimer: Always consult a professional mechanic if you’re unsure about diagnosing or repairing complex components like the turbocharger.