If you’ve ever wondered what gives modern diesel and gasoline engines that extra kick of power, the answer often lies in the turbocharger . This ingenious device has become a staple in automotive engineering, helping engines deliver more power while improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. But what exactly does a turbocharger do, and how does it work? In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about turbochargers, including their role in your engine and the mechanics behind their operation.
What Does a Turbocharger Do?
At its core, a turbocharger is designed to increase an engine’s efficiency and power output by forcing more air into the combustion chamber. Here’s how it accomplishes this:
- Boosts Air Intake: A turbocharger compresses air and delivers it to the engine at higher pressure, allowing more oxygen to mix with fuel.
- Improves Combustion: With more oxygen available, the engine can burn fuel more efficiently, producing more power per stroke.
- Enhances Fuel Efficiency: By extracting more energy from the same amount of fuel, turbochargers help reduce fuel consumption.
- Reduces Emissions: More efficient combustion also means fewer harmful byproducts are released into the atmosphere.
In short, a turbocharger allows smaller engines to produce the power of larger engines without sacrificing fuel economy or increasing emissions—a win-win for performance and environmental impact.
How Does a Turbocharger Work?
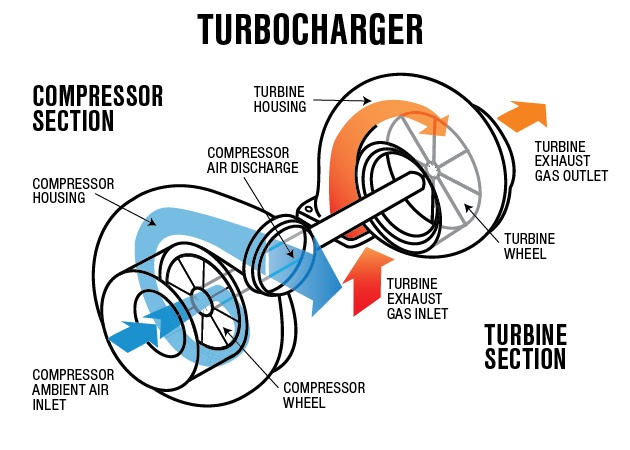
Now that we’ve covered what a turbocharger does, let’s dive into how a turbocharger works . The process involves two main components: the turbine and the compressor , both of which are connected by a shared shaft.
1. Exhaust Gas Powers the Turbine
The turbocharger uses exhaust gases—waste energy from the engine—to drive its turbine. As exhaust gases exit the engine, they pass through the turbine housing, causing the turbine wheel to spin at high speeds (often exceeding 100,000 RPM).
2. Compressor Forces Air into the Engine
The spinning turbine wheel is connected to the compressor wheel via a shaft. As the turbine spins, it drives the compressor, which draws in fresh air and compresses it before sending it into the engine’s intake manifold. This compressed air contains more oxygen, enabling more efficient combustion.
3. Intercooler Cools the Compressed Air
Compressing air generates heat, which can reduce its density and efficiency. To counteract this, many turbocharged engines use an intercooler to cool the compressed air before it enters the engine. Cooler air is denser, meaning it contains even more oxygen for combustion.
4. Wastegate Regulates Pressure
To prevent overboost—a situation where too much pressure damages the engine—a component called the wastegate regulates the turbocharger’s output. When boost pressure exceeds a safe limit, the wastegate opens, allowing some exhaust gases to bypass the turbine and reduce pressure.
Benefits of a Turbocharger
Understanding how a turbocharger works helps explain why it’s such a valuable addition to modern engines. Here are the key benefits:
- Increased Power: Turbochargers allow smaller engines to produce the same power as larger naturally aspirated engines.
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: By making better use of fuel, turbocharged engines consume less fuel under normal driving conditions.
- Reduced Emissions: More efficient combustion means fewer pollutants are released into the environment.
- Compact Design: Turbochargers enable manufacturers to use smaller, lighter engines without sacrificing performance.
Common Applications of Turbochargers
Turbochargers are used in a wide range of vehicles and machinery, including:
- Diesel Trucks: Turbochargers are standard in most diesel engines, where they enhance torque and towing capacity.
- Performance Cars: Many sports cars use turbochargers to achieve impressive horsepower figures.
- Industrial Equipment: Turbochargers are found in heavy machinery like tractors, bulldozers, and generators, where they improve efficiency and power output.
- Aircraft Engines: Turbochargers help aircraft engines maintain performance at high altitudes, where air is thinner.
Tips for Maintaining Your Turbocharger
To ensure your turbocharger operates at peak performance, follow these maintenance tips:
- Use High-Quality Oil: Clean, high-quality oil reduces the risk of contamination and ensures proper lubrication.
- Allow Proper Cool-Down Time: After driving, let the engine idle for a minute or two to allow the turbocharger to cool down.
- Inspect Regularly: Check the turbocharger and its components during routine maintenance to catch potential issues early.
- Replace Worn Components: Replace gaskets, seals, and oil lines as needed to prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance.
For more detailed information on identifying potential issues with your turbocharger , check out our blog post: Identifying Turbocharger Problems: Symptoms, Causes, and Solutions .
Conclusion
So, what does a turbocharger do , and how does a turbocharger work ? Simply put, a turbocharger enhances engine performance by compressing air and delivering it to the combustion chamber, resulting in more power, better fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. Understanding its function and mechanics can help you appreciate its importance and take steps to maintain it properly.
Whether you’re driving a turbocharged diesel truck or a high-performance sports car, paying attention to your turbocharger can save you time, money, and headaches in the long run. Have questions about turbochargers or need advice on replacements? Leave a comment below—we’re here to help!
Disclaimer: Always consult a professional mechanic if you’re unsure about diagnosing or repairing complex components like the turbocharger.